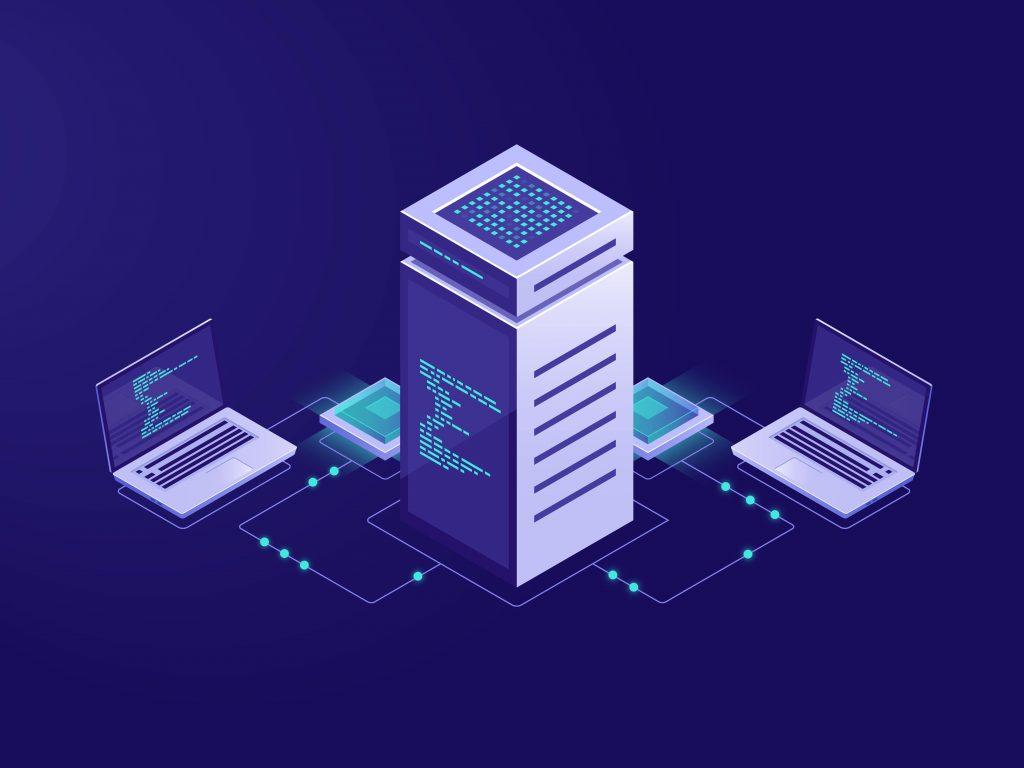
Blockchain is undeniably a disruptive force in the finance sector. It heralded a new era of decentralization over the traditional banking sector. “Bitcoin” and “cryptocurrency” are buzzwords that we have been adept with recently. Moreover, the conception of Bitcoin traces back to the devastating 2008 financial crisis. Blockchain technology is the future of banking, the backbone of Bitcoin, an aid for healthcare records, and a beacon for the supply chain.
Earlier, databases were an efficient way to manage data. So, how is Blockchain different from databases? Before delving deeper, let’s understand the basics.
The blog explains the definition of Blockchain and database and their benefits and puts light on Blockchain vs. normal database discussion.
What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a shared, immutable database or ledger distributed among nodes of a peer-to-peer network to record transactions and track digital assets across the business network. Moreover, Blockchain stores data in digital format. And a widespread implementation of Blockchain is in cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, for recording and maintaining transactions.
The fundamental objective of Blockchain is to store transactions in an immutable way. Hence, Blockchain is the foundation of immutable ledgers or records of transactions that cannot be altered or deleted. Therefore, blockchains are also called distributed ledger technology (DLT).
So, why is the network called Blockchain? Blockchains store information as blocks or chunks of linked data, forming a chain. Each block is immutable and has a capacity. On reaching the capacity, the network closes it and links it to the previous block.
What is Database?
A database is an organized collection of structured data stored electronically for easy access and management. Moreover, an administrator runs a database and has read, write, update, and delete permissions. DBMS (database management system) is a program that helps manage a database. A table is the basic unit of a database. Each table is a collection of rows and columns.
Moreover, databases use the client-server architecture. A client requests data, and the server that hosts the data authenticates the request and grants access. They follow a centralized network—generally, organizations store databases on servers in a single location. As a result, this can be a single point of entry.
What are the benefits of Blockchain?
There are different blockchains in the crypto-verse. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin are popular blockchains, amongst others. As the crypto world evolves, the blockchain grows in significance by the day.
Regardless of the blockchain, the following are their benefits:
Decentralization and automation
The foremost benefit of Blockchain is decentralization – there is no central authority or entry point to the system. The absence of a single entry point makes hackers challenging to gain access to the information. Moreover, transactions run on self-executing codes called “smart contracts,” increasing the overall performance. When a specific condition satisfies, smart contracts trigger the next transaction or process in line, reducing human intervention.
Enhanced Security
Blockchains generally maintain records of transactions. Hence, the information is valuable and must be secure. Blockchain stores data in blocks, forming a series of information. Moreover, the previous transactions are secure with encryption, and no one can modify them. As a result, the incidents of fraud and unauthorized access are reduced. Furthermore, blockchains are across different nodes, and there is no single entry point.
Greater Transparency
Blockchains use a distributed ledger for recording transactions; hence you can store the records at multiple locations. Moreover, all the users with permissions view the same information at the same time, thus, providing complete transparency.
Immutability
As we know, in blockchains, the network stores the transactions in blocks. And once you record the transactions, you cannot alter them. Hence, blockchains are immutable.
Quick Traceability
Blockchain records an audit trail that helps to document every asset’s journey. Thus, the records provide proof. Quick traceability renders blockchain several applications. For example, in the supply chain, blockchains enable finding the goods stuck up in transit and accelerating their delivery.
Increased speed and Efficiency
Traditional paper-heavy functions demand tremendous time and resources. Transferring these processes to blockchains can save time and money. Moreover, blockchains run on smart contracts that execute automatically on fulfilling specific conditions. Thus, reducing human intervention; decreasing human errors.
What are the benefits of the database?
Right from its inception, the database is a safe choice for the following reasons:
Customizable
The one point that makes the database win in the database vs. blockchain debate is – customizability. Databases offer more flexibility in terms of customization, as you can manage the databases centrally from one location with permissions and roles.
Stability
Blockchains run on nodes. And every node must record and verify the transactions. As a result, the system’s transactions per second decrease. So, the databases can manage high volumes of data and are more stable.
Backup
Databases provide a solid backup and recovery system. Backup is helpful in case of loss of data due to natural disasters, software failures, and human errors.
Speed
Over the years, databases have evolved from slower traditional databases to advanced client-server architecture. Also, compared to blockchains, databases are fast. Complexity and encryption can turn Blockchain slow and inconvenient.
Multi-user interface
Lastly, databases provide graphical user interfaces and application program interfaces to manage data better.
Is Blockchain similar to the database?
So, before delving into Blockchain vs. centralized discussion, let’s understand their similarities. Blockchain is similar to a database as it functions as a distributed ledger running on different nodes to store information blocks. On the other hand, a database is an organized structure for storing information. Whether the database is RDBMS or NoSQL, it provides a template to store data. To summarize, Blockchains and databases have a common objective – to store information.
Is Blockchain essentially a database?
Any structure that stores information is called a database. And the primary objective of Blockchain is to store information; hence it is a database. How is Blockchain different from traditional databases? Blockchains are different from databases in terms of how they store information. For example, blockchains store data in chunks of information called blocks. And once you store the data, it is irreversible. Moreover, the user can only append new transactions but cannot modify the existing ones.
On the other hand, databases don’t use signed blocks for storing information. Instead, they store information in tables. Although the Blockchain vs. RDBMS discussion is lengthy, we conclude that a blockchain can be a database, but a database cannot be a blockchain.
Difference between Blockchain and relational database
Blockchain and relational databases, or RDBMS, have their advantages and disadvantages. Furthermore, databases and databases have different applications. Understanding the difference between Blockchain and database is crucial to choose the right tool for your organization.
The following are distinctions that delineate the Blockchain vs. database debate:
| Points | Blockchain | Database |
| Structure to store data | Blockchain uses a decentralized structure to store data. | A database uses a centralized structure to store data. |
| Authority | Blockchains don’t need a central authority or admin. | A Database needs an administrator to manage data. |
| Permission | Blockchain can be permissionless. | A database needs read, write, and update permissions to modify data. |
| Immutability | Blockchains are immutable. You can only insert records and cannot modify or delete the records. | Databases support insert, modify and delete operations. |
| Security | Blockchains are more secure. | Databases are less secure as hackers can exploit a single point of failure to destroy the data. |
| Fault-tolerance | Databases are less fault-tolerant because they depend on a specific network of databases and admin. | Blockchains are more fault-tolerant as they don’t rely on a few servers for their operations. |
Conclusion
Blockchains combine the best of both worlds. You can consider it a database, but it is not similar to traditional databases. And the Blockchain vs. traditional database debate is subjective. And organizations should choose the right suit that aligns with their requirements and objectives. And those who can’t choose one can create a hybrid model combining both. And these hybrids are called blockchain databases, a secure, immutable chain of easily accessible blocks offering better performance.